Jan Vishwas Act: A New Era for Intellectual Property Rights in India
The recent amendments to intellectual property (“IP”) laws under the Jan Vishwas (Amendment of Provisions) Act, 2023, mark a significant shift in India’s IP regulatory landscape. These changes, which came into effect on August 1, 2024, aim to streamline processes, reduce compliance burdens, and foster a more conducive business environment. While the overarching goal is to promote ease of doing business, the implications of these amendments are far-reaching and require careful analysis.
Key Amendments
The amendments primarily focus on decriminalizing certain offenses, increasing penalties for some violations, and introducing new mechanisms for dispute resolution. The following table provides a comparative overview of the changes made to the Patent Act, Trade Mark Act, Copyright Act, and Geographical Indications Act:
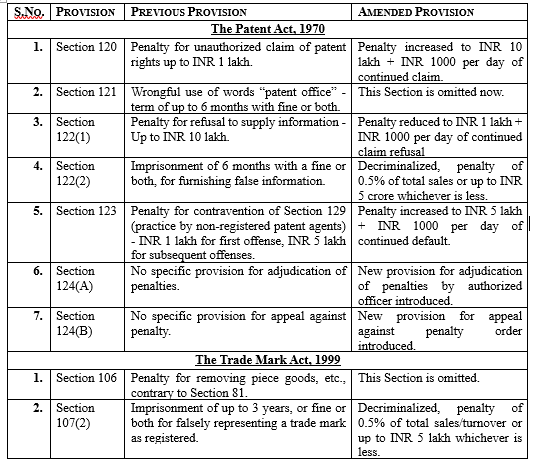
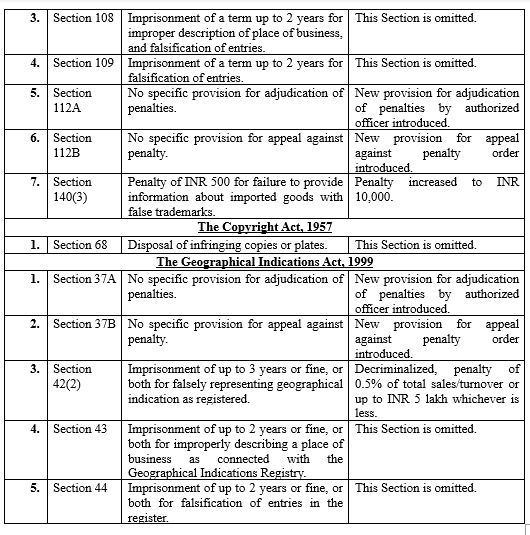
Implications and Analysis
The amendments reflect a shift towards administrative penalties and away from criminal sanctions for certain Intellectual Property (IP) violations. This approach is generally seen as a positive development, as it reduces the burden on the criminal justice system and allows for more proportionate penalties. However, concerns have been raised about the potential impact on public health and consumer protection, particularly in the context of patent infringement and false representation of trademarks. The introduction of adjudication and appeal mechanisms is a welcome step towards providing more efficient and transparent dispute resolution. However, the effectiveness of these mechanisms will depend on the qualifications and independence of the adjudicating officers.
Conclusion
Overall, the Jan Vishwas Act represents a significant overhaul of India’s Intellectual Property (IP) regulatory framework. While the amendments intend to create a more business-friendly environment, their long-term impact on innovation, public interest, and IP enforcement remains to be seen.
The amendments to India’s IP laws under the Jan Vishwas Act are a complex and multifaceted issue. While they offer certain benefits, such as reduced compliance burdens and streamlined dispute resolution, they also raise concerns about potential negative impacts on public health, consumer protection, and Intellectual Property (IP) enforcement. It is essential to carefully monitor the implementation of these changes and assess their impact on the overall IP ecosystem.
By entering the email address you agree to our Privacy Policy.