The Role Of Mediation And Arbitration In Legal Disputes

Mediation and arbitration are alternative dispute resolution (“ADR”) methods that allow parties to settle their disputes outside the traditional court system. Mediation involves a neutral third party, called a mediator, who helps facilitate communication and encourages the parties to reach a mutually agreeable solution. In contrast, arbitration involves an arbitrator who makes a binding decision based on the evidence presented.
In recent years, the popularity of mediation and arbitration has increased in India’s legal landscape. This rise can be linked to various factors, such as the growing burden on courts, the need for quicker and more efficient resolutions, and the potential for cost savings. These ADR methods provide a more amicable and collaborative approach to dispute resolution, making them appealing alternatives to litigation.
This piece will explore the rising role of mediation and arbitration in India’s legal system. It will highlight the advantages and challenges associated with these methods and consider their impact on the Indian legal environment.
Table of Contents
Mediation in India
Mediation is a voluntary process in which parties in a dispute work with a neutral third party, known as a mediator, to reach a mutually acceptable resolution. The mediator helps facilitate communication and encourages compromise.
The Mediation Act, 2023 represents a crucial development as India’s first independent legislation on mediation. Passed in August 2023, it establishes a framework aimed at promoting mediation as a viable dispute resolution method.
Key features of the Mediation Act include:
- A voluntary choice for parties to mediate civil and commercial disputes before going to court;
- Requirements for written mediation agreements covering all relevant disputes;
- Provisions for seeking interim relief in special circumstances;
- The establishment of the Mediation Council of India to set standards and register mediators; and
Mediation offers several advantages over traditional litigation, such as quicker resolutions, lower costs, and confidentiality, keeping discussions private.
Arbitration in India
Arbitration is a process where a neutral third party, called an arbitrator, is appointed to resolve a dispute. The arbitrator’s decision, known as an arbitral award, is binding on both parties and is usually enforceable like a court judgment.
The Arbitration and Conciliation Act, 1996 provides the main legal framework for arbitration in India. This Act outlines the procedures for conducting arbitration, appointing arbitrators, enforcing arbitral awards, and the limited grounds for challenging those awards.
Choosing the right arbitrator is crucial. Parties can either agree on their choice or use established institutions like the International Chamber of Commerce (“ICC”) to facilitate the appointment.
The arbitration process generally includes exchanging pleadings, presenting evidence, and making oral arguments. After considering the information, the arbitrator issues an award. These awards are typically enforceable both in India and internationally, although they can be challenged on specific grounds such as fraud or public policy issues.
Arbitration has several advantages compared to traditional litigation. It tends to be more efficient and cost-effective, bypassing the lengthy court procedures. Additionally, parties can select arbitrators who have expertise in the relevant area, ensuring a knowledgeable resolution of the dispute. Another benefit is confidentiality, as arbitration proceedings are usually private.
Mediation vs. Arbitration
Mediation and arbitration are both methods for resolving disputes, but they have some important differences. These are as follows:
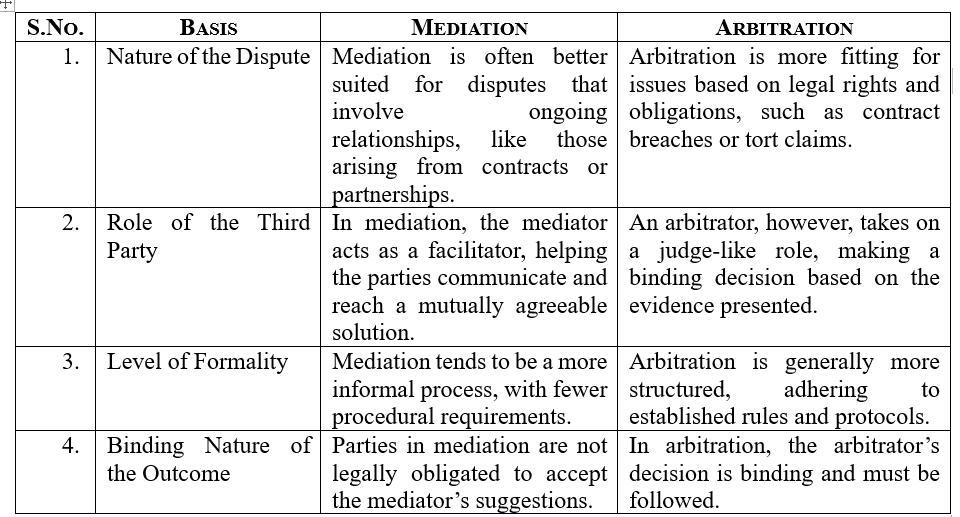
The choice between mediation and arbitration will depend on various factors, including the type of dispute, the relationship between the parties, and the desired outcome. In some situations, combining both methods in a process known as med-arb can be beneficial.
The Future of Mediation and Arbitration in India
Mediation and arbitration are set to become increasingly important in India’s legal landscape. Several factors are contributing to this growth, including the rising pressure on courts, the need for more efficient dispute resolution, and a greater recognition of the advantages of amicable settlements.
A notable trend in this space is the growing use of technology. Online dispute resolution (“ODR”) platforms are gaining traction, allowing parties to resolve disputes remotely. Additionally, artificial intelligence (“AI”) is being introduced to assist with tasks like document review and negotiation.
Recent legal reforms have also positively impacted ADR. For example, the Commercial Courts Act, 2015 established specialized commercial courts to manage business disputes more effectively, helping to alleviate the backlog in regular courts.
Conclusion
Mediation and arbitration are increasingly vital in India’s legal system, allowing parties to resolve disputes outside traditional courts. Mediation fosters collaboration and open communication, while arbitration provides a binding decision for legal matters. The recent Mediation Act, 2023, and ongoing legal reforms are boosting the credibility of these ADR methods. With technology playing a growing role, such as through online platforms and AI tools, these processes are becoming more accessible. However, ensuring that mediators and arbitrators are well-trained is essential. By raising awareness and developing ADR frameworks, India can enhance its dispute resolution mechanisms, benefiting both individuals and businesses.
King Stubb & Kasiva,
Advocates & Attorneys
New Delhi | Mumbai | Bangalore | Chennai | Hyderabad | Mangalore | Pune | Kochi
Tel: +91 11 41032969 | Email: info@ksandk.com
By entering the email address you agree to our Privacy Policy.